Meteorology is all about weather and its forecasts. And the whole foundation of meteorology lies in weather instruments that help forecasters predict the weather conditions.
If you are a weather geek, you might always have wondered about different weather instruments and their usages. Right??
To help, we have prepared this handy guide to help you learn more about different instruments and their usage in meteorology space. Let’s dive right in…
What Are Weather Instruments?
Weather instruments are devices that measure weather-related conditions. They are used to gather data on wind speed, precipitation, temperature, humidity, and other factors. Weather instruments are essential in helping meteorologists analyze and evaluate the data collected by many different types of weather monitoring devices.
The Significance of Weather Instruments
The significance of weather instruments can be understood by considering that without them, it would be difficult for meteorologists to monitor the changes in weather patterns over time. In addition, it would be impossible for meteorologists to determine how severe or prolonged a storm will last without an accurate reading from a given instrument.
They help them forecast weather conditions for the next few days, weeks, months, or years ahead.
8 Top Weather Instruments that Meteorologists Use to Predict Weather
Below we have listed the top weather instruments used to predict the weather in Meteorology.
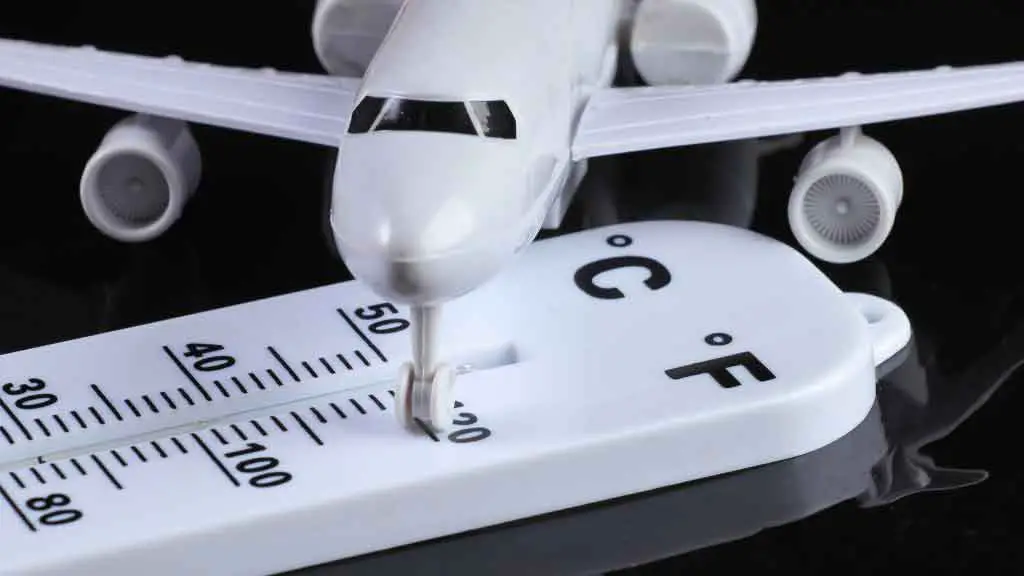
1. Thermometer
What Is a Thermometer?
A weather thermometer is a device used to measure the temperature of the air. It does this by measuring the temperature of a column of air in the atmosphere.
What Does Thermometer Measure?
Weather thermometers measure atmospheric pressure. Pressure is the force exerted by atmospheric molecules on objects. The higher the pressure, the lower the temperature. A weather thermometer can be used to determine if there are clouds or not, what direction they are moving in, and how heavy they are. All things that affect air temperatures!
Types of Thermometers
The different types of thermometers used in weather stations are:
- Mercury Thermometer
- Resistance Thermometer
- Bi-metallic Strip Thermometer
- Constant Volume Thermometer
How Does Thermometer Work?
The weather thermometer measures the air temperature near its surface and then uses this data to calculate the actual air temperature. This calculation is done using algorithms developed by scientists to ensure accuracy.

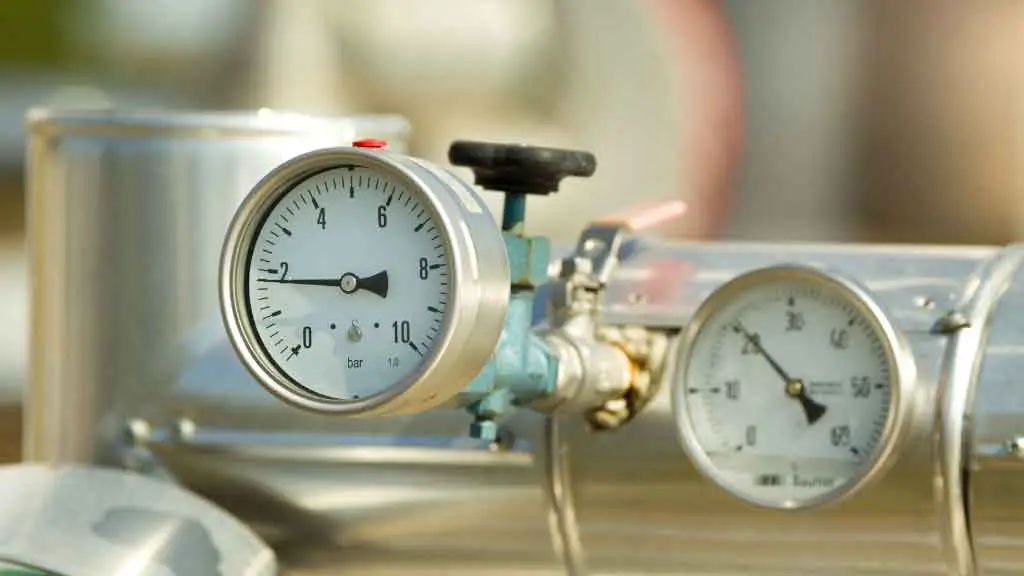
2. Barometer
What is a Barometer?
A barometer is a device that measures atmospheric pressure. It is used by meteorologists (and pilots) to predict weather conditions and by farmers to determine if there will be sufficient rain during the season.
What Does Barometer Measure?
A barometer measures atmospheric pressure in millibars (mb) or hectopascals (hPa). The higher the barometric pressure, the more gravity squeezes air molecules together. A decrease in pressure results in an increase in height because all of the air above a given point has had to go down to fill all of the space between it and that point. This happens because when there is less air above an object, it can hold more weight than when there is more air above it.
Types of Barometers
A few barometers are available: mechanical, electronic/digital, and hand-held.
Mechanical barometers are simple devices that rely on a weighted glass bulb to indicate changes in air pressure. Electronic/digital barometers use sensors to detect changes in atmospheric pressure and send signals to display screens or speakers so you can see them directly on your device instead of looking at something like a thermometer or hygrometer (which measures humidity). Hand-held barometers are simple devices that measure air pressure by holding up two fingers against a balloon until it pops; however, they’re less accurate than other types.
How Does Barometer Work?
A barometer measures atmospheric pressure in several ways. One way is through an aneroid barometer, which uses mercury instead of air as its fluid. When air molecules get squished together, they create negative pressure, which pushes up on the mercury column inside the instrument (the column rises due to negative pressure).

3. Hygrometer
What is a Hygrometer?
A hygrometer is a device that measures the relative humidity in an environment. It can be used to detect the moisture content of a room, and it can also be used to measure humidity levels inside a home or office. The hygrometer uses a combination of capacitance and resistance to measure the moisture content of air, which is then displayed digitally on an LCD screen.
What Does a Hygrometer Measure?
The amount of water vapor in the air at any given time is measured by a hygrometer, which can be used for checking the relative humidity level in different areas of your home or office.
Types of Hygrometer
There are three types of hygrometers: wet bulbs, dry bulbs, and electronic sensors. Wet-bulb hygrometers use water to measure humidity levels; they have a glass bulb filled with water that contains a thermometer and scale built into its surface or body. Dry bulb hygrometers use a thermometer inside an open tube with a metal ball suspended inside; as more moisture evaporates from your surroundings into this tube, so does the metal ball inside it changes position within its tube.
E-type hygrometers are very accurate but cost more than their mechanical counterparts; therefore, they’re not widely used nowadays because they’re expensive compared with other options available today.
How Does a Hygrometer Work?
Hygrometers rely on two different types of technology: thermopile and resistivity sensing. Thermopile technology uses semiconductors to sense heat from a human body (or other warm objects). Resistivity sensing uses an electrical current that changes when there is more or less moisture than usual in the air (or another medium).

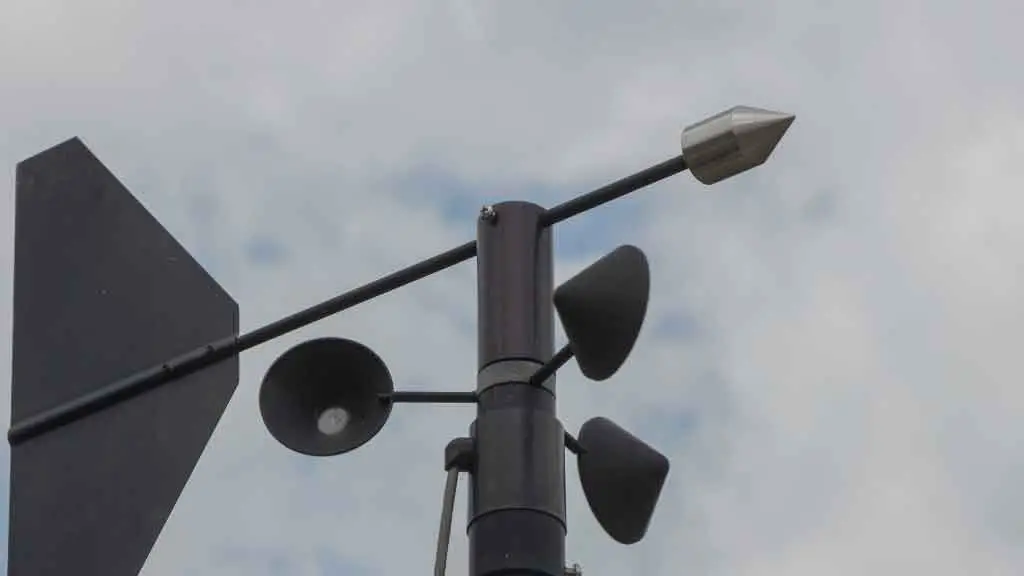
4. Anemometer
What is an Anemometer?
An anemometer is a weather meter that measures wind speed and direction. It can measure wind speed and direction at various heights above ground level.
An anemometer measures the wind speed and direction in the form of a horizontal bar with two or more vanes or blades, which are made up of thin metal plates attached to a vertical shaft or armature. These vanes move in response to changes in atmospheric pressure caused by the movement of air across them as it moves through the atmosphere.
What Does an Anemometer Measure?
An anemometer measures how much air moves in different directions at different speeds. The faster the air moves, the more power it takes to keep it moving. This power is called kinetic energy (KE), measured in J/kg.
An anemometer measures static pressure, which is force per area (N/m2). Static pressure measurements can determine whether there’s enough water vapor in the air for the rain to fall or if there aren’t enough vapors for clouds to form and produce precipitation; this is called the “precipitation requirement.”
Types of Anemometer
The four most common kinds of Anemometer are:
- Vane Anemometers
- Thermal Anemometers
- Thermal Anemometers with Velocity
- Cup Anemometers
Fixed-wing and rotary-wing models of Anemometer are also widely used.
Fixed-wing anemometers are less expensive than rotary-wing models, but they require careful installation because they have no moving parts, so they cannot be moved once installed on the aircraft’s wing surfaces; instead, they must be installed permanently on the wing surfaces themselves.
How Does An Anemometer Work?
Understanding the working of an anemometer is normal. Here’s how it works:
An anemometer consists of a hollow needle and a rotor inside it. The rotor has blades that rotate due to the wind blowing over them. These blades cause air to flow through it, creating pressure differences on each side, which are measured by a set of vanes on either end of the rotor. This pressure difference causes a constant rotation in the vanes, which creates an electric current in an ammeter attached to them. A scale on top of this meter shows current flowing through it under each set of vane blades.
Anemometers measure the rotation of a shaft or rotor in an airstream. This air stream can be captured with a tube or pipe open at one end. The wind blows through this tube, which causes it to rotate. This motion is detected by an attached mechanical indicator, which indicates how much air has flowed through the tube since it was last opened and closed again.

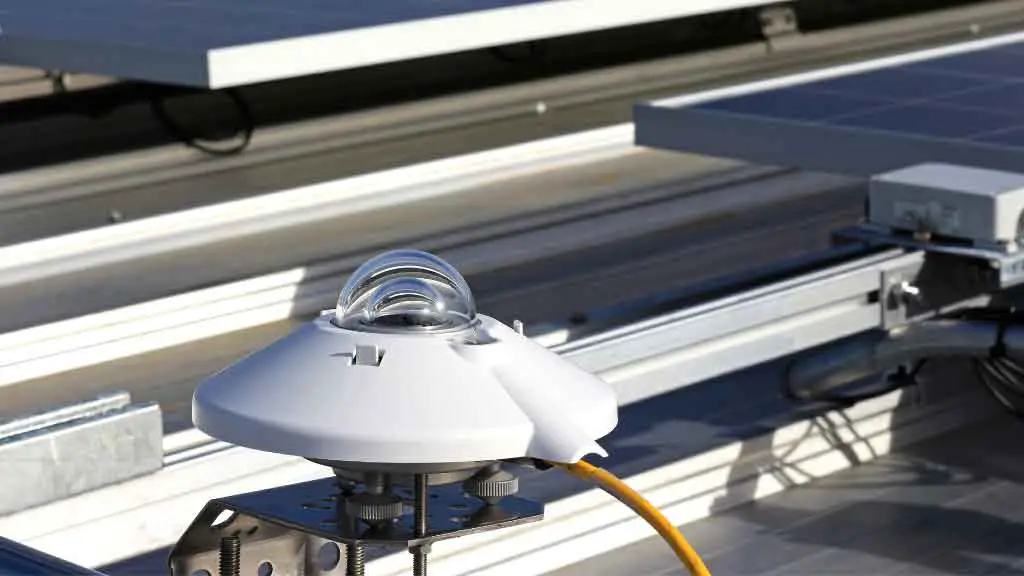
5. Pyranometer
What is Pyranometer?
A Pyranometer is a device that measures the amount of solar radiation (also known as direct solar radiation) hitting a surface. It does this by measuring the temperature of the air in the atmosphere and converting it into energy. This energy is then measured by a thermocouple, which converts the heat into a voltage that an ammeter can measure. The unit is also known as a thermopile and has two thermocouples attached.
What Does a Pyranometer Measure?
Pyranometers measure total solar radiation and its components: diffuse reflected and direct irradiance. They are also used for measuring the solar constant, which is equal to 1/7th of incident light power on the earth’s surface per unit area. This value is useful for calculating global mean temperatures from observations taken at high latitudes or satellites orbiting closer to the earth’s orbit than other satellites (such as weather satellites).
Types of Pyranometer
There are three major types of pyranometers: fixed-film based, floating-film based, and rotating-film based. Fixed film
How Does a Pyranometer Work?
A pyranometer works based on the measurement of temperature differences between two surfaces. One is a transparent surface, and the other is a dark surface.
The clear surface of the Pyranometer reflects the sun’s radiations. Hence, it absorbs a smaller amount of solar radiation. At the same time, the dark surface of the Pyranometer absorbs solar radiation. The difference in radiations between the two surfaces is what a Pyranometer measures. Some Pyranometers have an analog interface to generate reading signals, while others feature a digital interface.

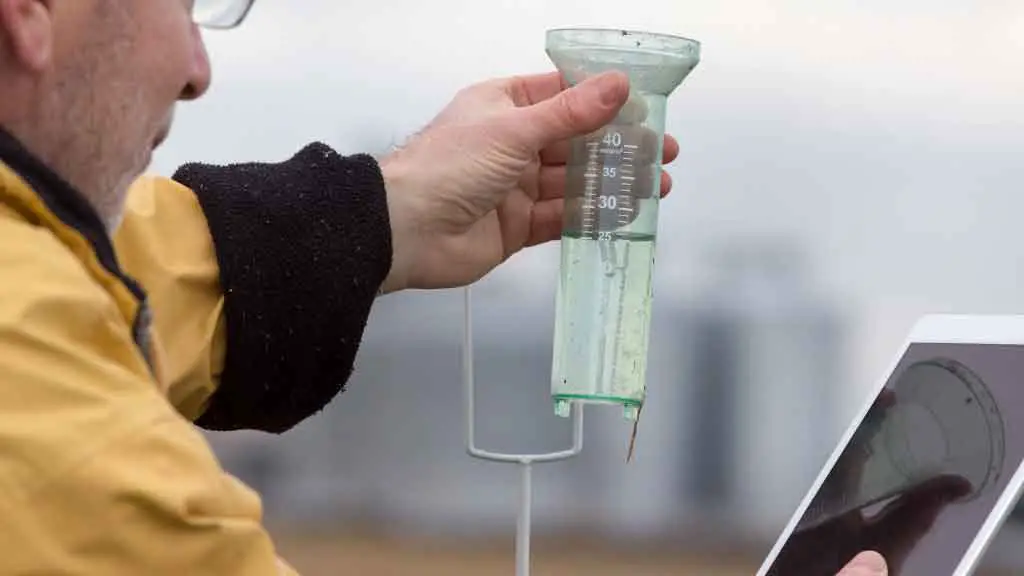
6. Rain gauge
What is a Rain gauge?
A rain gauge is a device used to measure the amount of precipitation that falls on a particular area over a period of time. Rain gauges are very useful in weather forecasting; meteorologists often use them to determine how much water has fallen during a storm. Rain gauges can be either stationary or portable.
What Does Rain Gauge Measure?
Rain gauges measure precipitation using porous material such as felt or textile fabric to absorb the rainwater. When the rain falls on this material, it becomes saturated and fills up with water. This moisture is then collected in another container (the “collecting chamber”) for later analysis.
Types of Rain gauge
Commonly, there are three main types of the rain gauge.
- Standard Gauge
- Tipping Bucket Gauge
- Weighing Gauge
Standard Gauge: The rain is measured manually in the funnel-shaped rain gauge.
Tipping Bucket Gauge: The working of the tipping bucket gauge is different from the standard gauge as its receiving funnel features two small buckets at the end.
Weighing Gauge: The weighing gauges are precise in calculating the intensity of the rain.
How Does Rain gauge Work?
A standard rain gauge features a funnel-shaped corrector attached to a measuring tube.
While gauging the rain, the instrument catches the rain in the collector. The area of the collector is 10x more significant than the measuring tube. Hence, the rain gauge magnifies the liquid by a factor of 10.
When the amount of rain exceeds the limit of the tube, it is then caught in the outer shell of the rain gauge. This excess amount is filled back in the tube if the need arises.

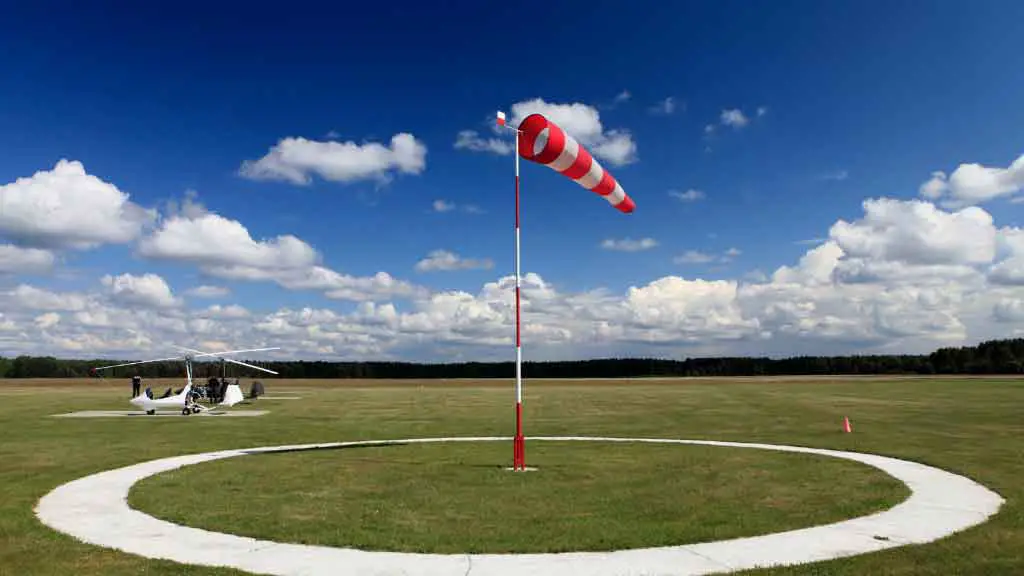
7. Windsock
What is Windsock?
A wind sock is a wind measuring device used to measure wind speed and direction. It consists of a horizontal tube with two floats attached at either end of the tube. The tube is filled with air and then tilted at an angle to the wind. The force of the wind on one side of the tube will cause it to be deflected downward, while the force on the other side will cause it to be deflected upward. An observer can use this data to estimate wind speed and direction.
What Does Windsock Measure?
A common misconception about windsocks is that they measure air temperature, but this is not true. They measure wind speed and direction, which has nothing to do with air temperature or humidity levels. However, they provide useful information in conjunction with weather stations. For example, you can use your outdoor thermometer as part of a rain sensor system by placing it inside a window well so that it can’t be seen from outside but still measures outside air temperature (and thus rain rate).
Types of Windsock
There are two main types of windsocks:
- L-806
- L-807
The type of the windsock generally depends on the way it’s mounted. But, the assembling procedure of the windsock types is different.
How Does Windsock Work?
A windsock is a conical textile tube resembling a sock’s structure.
The wind enters this sock from one end and escapes from the other. And the latter end of the sock points it in the opposite direction from where the wind had entered the sock.
Say, if the wind entered from the end pointed towards the west while escaping, the latter end would point towards the east.

8. Wind Vane
What is a Wind vane?
A wind vane is a small propeller-like device mounted on the top of a mast or tower that points into the wind. A horizontal axis connects the base of the blade to a vertical axis below it. This allows it to spin freely in the breeze but not turn around its own axis. The user can read the direction and speed of the wind by observing where the blade points.
What Does Wind Vane Measure?
The number of times per second that the vane moves up and down. A vane can measure other things besides just wind speed or direction. For example, a pressure sensor at one end can detect air pressure changes caused by winds. An electric motor can be used to turn a shaft that pulls on a weight system at the other end, or an optical sensor could be used to detect light from stars or the moonlight shining through clouds above or around you.
Types of Wind Vane
Majorly there are two types of the wind vane.
- Classic Weathervane
- Digital Wind Vane
Windsock is also a kind of wind vane.
How Does Wind Vane Work?
The wind vane is mounted on a shaft (typically), which is above ground level. When the wind captures the rudder blade, the rudder blade starts rotating. The narrow end of the Wind vane then points in the direction the wind is coming from.
What is the most helpful weather instrument?
The barometer is the most helpful weather instrument. The barometer measures atmospheric air pressure and is used to predict the weather. The proper functioning of the barometer can be affected by several factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and pressure changes concerning altitude. The barometer can be used to predict the weather conditions at a specific location over some time.
Barometers are mainly divided into two types: The mercury barometer, which uses a liquid column (usually mercury), and the aneroid barometer, which uses a series of aneroids or weighted balls suspended in the air to measure pressure changes. These are generally referred to as wet-bulb and dry-bulb indicators, respectively.
Weather Stations
Many instruments work together in a weather station. These instruments predict weather conditions, such as temperature, precipitation, wind speed and direction, and pressure.
The most common instruments are Anemometer, pressure sensor, thermometer, wind vane, Hygrometer, and rain gauge. The instruments are formatted to support WMO to help weathercast prediction.
Some Fun and Easy-to-Understand Facts About Weather Instruments
Here are some fun facts that you must know about weather instruments:
- A hundred years ago, weather forecasting instruments were as complicated as the barometer/thermometer and as simple as your five senses.
- Weather balloons measure weather patterns (high over the Earth level).
- A few weather stations have sensors to measure rainfall. They can be on land or at sea. Currently, there are over 10.000 weather stations in the world.
- Your eyes are also one of the best ways to measure weather conditions. So, don’t forget to keep an eye on the sky.
FAQs:
Q1. What are the different weather instruments?
Ans. Different weather instruments used to predict weather are Anemometer, wind vane, rain gauge, hygrometer, and thermometer.
Q2. What is the weather gauge called?
Ans. A weather gauge is also known as an udometer, pluviometer, pluva metior, hyetometer, and ombrometer.
Q3. What weather does the instrument measure wind?
Ans. An Anemometer measures wind’s speed and pressure.
Q4. What instrument measures dew?
Ans. The instrument that measures dew is known as Psychrometer.
You might be interested in: Climate change what everyone needs to know
Final Words:
That’s all we had to say about weather instruments in the definite guide.
We hope you have found all the answers to the queries you had in your mind about weather instruments, weather stations, and helpful weather instruments. So, if you have questions about weather instruments that we haven’t answered in the guide, write to us in the comments below.

















